The following information will help when working with BACnet devices and networks and your EMH datalogger.
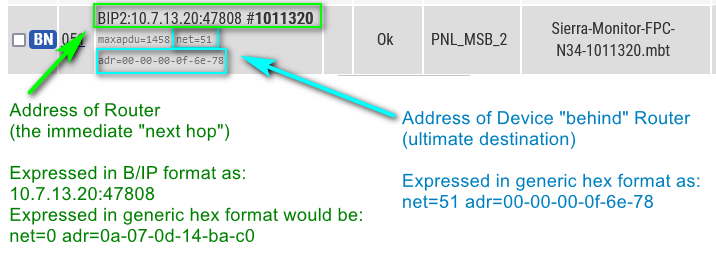
The following diagram helps illustrate how to interpret what you are seeing in our Devices page when a BACnet device is associated to the logger.
All BACnet addresses can also be displayed in a generic format, which is:
The B/IP address 10.7.13.20:47808 (in IP format) could be displayed in two formats:
The BACnet/MSTP data link uses 1 byte addresses, so a typical B/MSTP address might be:
Common abbreviations you may come across in the BACnet world are SNET, SADR, DNET, DADR.
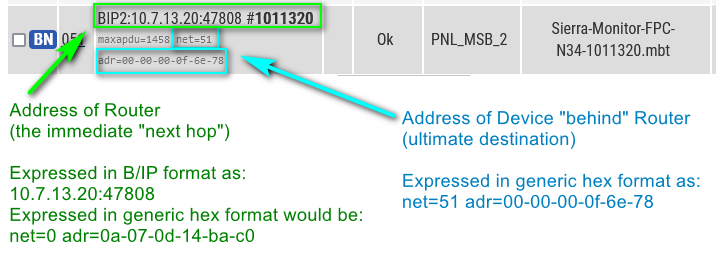
The following diagram helps illustrate how to interpret what you are seeing in our Devices page when a BACnet device is associated to the logger.

All BACnet addresses can also be displayed in a generic format, which is:
- Net = 16-bit integer, where 0 means “this (local) network”.
- Adr = 1 or more bytes, in hex, separated by dashes.
The B/IP address 10.7.13.20:47808 (in IP format) could be displayed in two formats:
- Net = 0
- Adr = 0a-07-0d-14-ba-c0 ( hex version of 10.07.13.20 : 47808 )
The BACnet/MSTP data link uses 1 byte addresses, so a typical B/MSTP address might be:
- Net = 0 or network number
- Adr = 7F ( hex version of device with MSTP unit # 127 )
Common abbreviations you may come across in the BACnet world are SNET, SADR, DNET, DADR.
- SNET and SADR is a BACnet _source_ { network number and address }.
- DNET and DADR is a BACnet _destination_ { network number and address }.